Osterwalder's business model is an effective strategic management tool that allows you to describe and analyze business models of organizations. This approach is useful for both new companies and established ones.
For startups and early stage companies, the model helps assess the current market position, identify growth prospects, and conduct competitor analysis. Organizations with established positions can use the model to identify weaknesses in their operations and promptly make necessary changes.
How to Write an Osterwalder Business Model: Key Steps
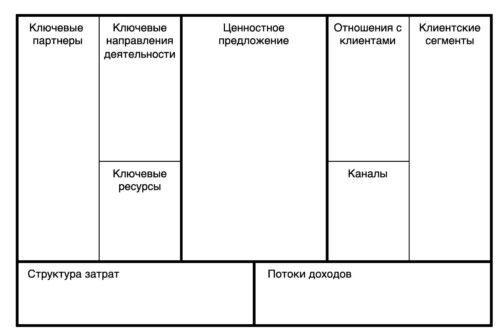
Osterwalder's business model consists of 9 main blocks that help to work out the company's strategy in detail:
- Consumer segments. Defining the target customer groups your products or services are aimed at.
- Value propositions. Formulating unique advantages that distinguish your company from competitors.
- Distribution channels. Ways and methods of delivering goods or services to your customers.
- Customer relations. A customer engagement strategy aimed at attracting and retaining an audience.
- Income streams. The main sources of income of the company.
- Key resources. Important assets necessary for the successful operation of a company.
- Key activities. The core processes and tasks that deliver the value proposition.
- Key partners. External companies or organizations that support your activities.
- Cost structure. Analysis of expenses associated with business management
These blocks help to get a complete picture of the current state of the company and develop effective solutions to achieve goals.
Let's consider the principles of filling the blocks of the Osterwalder model
Filling in each of the 9 blocks of the business model requires detailed analysis and a strategic approach. Let's consider the sequence and basic principles of working with each of them:
Customer Segments
A customer segment is a group of people or organizations that share common problems, needs, or characteristics. This block of the business model describes who the product or service is created for.
Why is it important to define customer segments?
Accurately defining your target audience is the key to successful advertising campaigns, developing effective sales strategies and increasing customer loyalty.
How to work with this block?
To properly describe customer segments, answer the following questions:
- Who are our clients? Describe for whom the products are created, services are provided, or goods are manufactured. These may be individuals, companies, or specific interest groups.
- What are the characteristics of our target audience? Create a brief profile of the client: age, profession, income level, interests, geographic location, etc.
- Is it easy to find target customers? Assess how easy it is to reach your target audience through advertising, social media, or other channels.
- Which customer group is most important to your business? Identify the core segment that generates the most profit or provides the most value to the business.
A thorough analysis of customer segments allows you to develop a value proposition that will be as relevant as possible to the needs of the target audience.
Value Propositions
A value proposition is the key reason why customers choose your product or service over your competitors. It describes the specific problems you solve and the needs you meet, highlighting the uniqueness of your offering for a specific customer segment.
Why is value proposition important?
It helps you identify what makes your product useful and attractive to customers. A clearly articulated value proposition improves brand perception, builds trust, and increases conversion.
How to formulate a value proposition?
Answer the following questions:
- What value do we create for our clients? Highlight the key benefits of your product or service. These could be time savings, cost reduction, convenience, or exclusivity.
- What customer problems do we solve? Identify specific problems or pain points of your target audience that your product helps to solve.
- What customer needs do we satisfy? Ask yourself what your customers want and how your product helps them achieve it.
- What does our offer consist of? List all the elements that are included in your offer: services, products, service, support, etc.
Distribution channels (Channels)
Distribution channels are all the ways and means through which a company interacts with customers at all stages: from informing about the product to post-purchase service. Effectively built channels help ensure a positive customer experience and increase the likelihood of repeat purchases.
The main stages of working with channels:
- Informing. How do you communicate information about your product or service to your target audience? This could be through advertising campaigns, social media posts, email newsletters, participation in exhibitions or partnerships.
- Grade .How do customers know what makes your product different from competitors? Use your website, testimonials, demos, free trials to highlight the benefits.
- Sale. How does the purchase process take place? It can be an online store, an offline store, marketplaces or personal consultations. Simplicity and convenience of the process play a key role here.
- Delivery and adaptation. How do you organize the delivery of a product or the provision of a service? Fast delivery, high-quality packaging, and the ability to easily adapt to the product form a positive first impression.
- Service. What do you do to support customers after purchase? This could include a hotline, warranty service, loyalty program, or periodic communication.
Questions to fill in the block:
- Which channels are best for connecting with customers?
- How do we interact with clients now, and how effective is it?
- Which channels are the most profitable?
- How can you improve the customer experience at every stage of interaction?
Customer relationships
Customer relationships are various formats of interaction with the target audience that ensure the attraction, retention and satisfaction of customer needs. Properly built relationships help to strengthen trust, increase loyalty and increase the company's revenue.
Main types of interaction:
- Personal support. This is done through direct contact with the client, such as consultations, technical support or assistance at all stages of the transaction.
- Self-service. It assumes that the client can independently obtain all the necessary information or make a purchase through the website, chat bots or automated systems.
- Free or shareware use. Involves providing basic services or features for free, with the option to purchase additional options. This approach is often used in SaaS models.
- Co-creation. Customers participate in the creation of a product or service by providing feedback, ideas, or creating content. For example, user reviews, photos, or videos that a company uses in marketing.
- Individual or group training. Educating customers on how to use a product or service through seminars, courses, webinars or training materials.
Formats of interaction depending on business objectives:
- Attraction for a one-time purchase. Suitable for businesses with infrequent purchases, where it is important to quickly interest the client, demonstrate the value of the product and close the deal.
- Retention for long-term cooperation. Used for businesses focused on repeat sales or long-term contracts. For example, loyalty programs, bonus systems or high-quality after-sales support.
- Specialization for certain categories of clients.Relationships are tailored to the unique needs of specific groups, such as luxury car owners or customers with a specific set of requirements.
Questions to fill in the block:
- What kind of relationship do customers expect based on your product or service?
- What interaction model are you using now?
- Are your existing relationships aligned with your business strategy?
- What tools can help improve customer experience?
Revenue streams
Revenue streams describe how your business makes money and what monetization models are used for each customer segment. This block helps you understand what brings in the bulk of your revenue, as well as what additional sources you can use to increase your profits.
Main models of income generation:
- Sale of goods. The classic model in which a business makes money by selling physical or digital products to end users, distributors or dealers.
- Fee for using the service. Revenue is generated based on the volume or time of service use. Example: web development services, where the price is calculated based on the volume of work or hours spent on the project.
- Subscription payment. A fixed fee for access to a product or service for a certain period of time. Often used in SaaS, streaming services, or fitness clubs.
- Rent. Temporary transfer of ownership of a specific asset for a set amount. Example: leasing equipment, cars or servers.
- License. Income from the provision of rights to use intellectual property (patents, copyrights, software) for a limited period.
- Commission. Businesses earn money as intermediaries, receiving a percentage of the transaction. Example: marketplaces that charge sellers a commission for each successful transaction.
- Advertising. Earning income for placing advertising materials on the company's platform. For example, banners on a website or embedded advertising in applications.
Pricing mechanisms:
Each revenue stream has its own pricing model, which depends on the value proposition, competition, and the characteristics of the target audience. Possible approaches:
- Fixed price (for example, subscription).
- Dynamic pricing (eg auction prices).
- Differentiated prices (depending on purchase volume, loyalty or customer specifics).
Questions to fill in the block:
- What products or services are customers willing to pay for?
- What value do they get when they pay for your product?
- How do they pay now and what would they prefer to pay by?
- Which payment channels are most convenient for your audience?
- How is the contribution of each revenue stream distributed to the company's overall profit?
Key Resources
Key resources are the assets that are essential to the successful operation of the business model. They support the creation of the value proposition, the operation of the distribution channels, customer interactions, and revenue generation.
Why are key resources important?
These resources provide the foundation for creating products and services, helping a business stay competitive and driving long-term growth. Understanding and managing key resources effectively allows you to optimize your business.
What are the key resources?
- Material resources: These are physical assets: equipment, raw materials, transport, retail outlets, offices and warehouses.
- Intellectual resources: Intangible assets such as brands, patents, copyrights, technology, databases and software.
- Staff: A team of specialists with the knowledge and skills needed to complete business tasks. These may be managers, developers, marketers, and others.
- Financial resources: Cash, working capital, loans, investments and other sources of financing.
How to identify key resources?
Answer the following questions:
- What resources are needed to create a value proposition?
- What assets are needed to interact with customers and operate distribution channels?
- What resources help maintain competitive advantages?
Key Activities
Key activities are the core operations and processes that enable the creation, delivery, and maintenance of value propositions. They describe, how exactly your business is functioning and achieving its goals.
Why are key activities important?
It defines what efforts and actions are needed to maintain competitiveness, satisfy customer needs and grow the company. A clear understanding of key actions helps to optimize resources and processes.
Types of Key Activities
- Production: For companies that create goods, this includes raw material procurement, logistics, manufacturing processes, quality control and delivery.
- Problem solving: Suitable for service companies. Includes diagnostics, knowledge management, employee training, research and customer satisfaction analysis.
- Infrastructure management: For platforms, applications and services, this includes development, testing, technical support, user experience management and planning of new features.
How to define key activities?
Answer the questions:
- What actions are needed to create a value proposition?
- What processes are essential to keeping a company running?
- What is done on an ongoing basis to improve the quality of work and retain customers?
Key Partners
Key partners are companies and organizations that your business partners with to operate and deliver your value proposition. They provide resources, services, or perform tasks that you cannot or do not plan to perform on your own.
Why are key partners important?
They help reduce costs, minimize risks, optimize processes and focus on core operations.
How to identify key partners?
Answer the questions:
- What partnerships allow us to work more effectively?
- What resources or services do we receive from partners?
- What tasks can be delegated to partners while maintaining quality?
Types of key partnerships:
- Strategic Alliances: Collaborating with other companies to achieve shared goals (e.g. co-branding or creating joint products).
- Suppliers: Companies that supply materials, equipment or services needed for your business.
- Outsourcing: Transferring individual processes (e.g. logistics, accounting or marketing) to third parties to increase efficiency.
- Platforms or networks: Using third-party platforms to increase reach (e.g. marketplaces or ad networks).
Cost structure
This block records all expenses related to creating value propositions, maintaining business processes, and interacting with clients. Cost analysis helps optimize the budget and determine which elements require the greatest investment.
How to determine cost structure?
Answer the following questions:
- What are the main costs associated with producing a product/service?
For example, purchasing raw materials, paying wages, renting premises. - Which resources cost us the most?
This could be technology, infrastructure, people or materials. - Which activities require the most investment?
Identify processes that require large investments - production, marketing, logistics, research.
Types of costs:
- Fixed costs:
Fixed costs that do not depend on the volume of production.- Rent of office or industrial premises.
- Salaries of employees (administrative staff).
- Equipment depreciation.
- License fees.
- Variable costs:
Costs that vary with production or sales volume.- Raw materials and supplies.
- Payment of wages to temporary employees.
- Logistics and delivery.
- Commission to partners or platforms.
The Osterwalder Business Model is a versatile tool that helps create a holistic view of a company's operations by structuring key aspects of the business on a single page. It includes elements such as value propositions, customer segments, distribution channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, partners, and cost structure. This tool is popular due to its simplicity and clarity: it is easy to fill out even without being an expert in strategic planning, and all the important aspects of the business are collected in one place, which allows you to quickly see the big picture and identify weak points that require attention or optimization. The Osterwalder Business Model is suitable for both startups and large corporations, it helps analyze the current business, develop new strategies, and find opportunities for growth.
So, you have become familiar with Osterwalder's business model, which helps to structure business processes and create value for the client.
How do you know if Osterwalder's model is right for your company, or if you should pay attention to Alexander Pankov's authorial approach?
Sometimes standard solutions can miss the individual characteristics of a business, while unique methods provide new growth points. To choose the right tool, it is important to study different approaches and their application in practice.
Want to learn more about how to create a sustainable and profitable business model using the Pankov Method? Follow the link and read about the author's method "8K-matryoshka".
We also recommend that you learn more about "Roasting the current business model" how to improve your business model to help your business achieve its goals and solve the necessary problems.