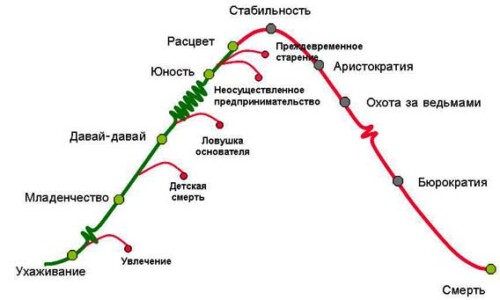
The Adizes methodology presents an organization as a living organism that goes through various stages of development and aging. Understanding the current stage of the company's life cycle helps owners and top managers make informed strategic decisions, adjust processes for successful functioning, and direct the company to a sustainable path of development. In this article, we will examine in detail the key characteristics and recommendations for each stage of the organization's life cycle.
According to Adizes, every company goes through several stages of its development:
- Courtship
- Infancy
- Come on, come on
- Youth
- Flourishing
- Stability (or Late Bloom)
- Aristocracy
- Witch Hunt (or Early Bureaucracy)
- Bureaucracy
- Death
1. Courtship
At this stage, the idea for the business is born and the founder is enthusiastic. This is the dreaming and conceptualizing phase, when it is important to set the direction and develop a vision for the company.
Characteristic features: The idea is in the discussion stage, the founder is developing a vision and analyzing prospects.
Possible problems: Lack of concrete actions, excessive theorizing, poorly developed business model.
Recommendations: Assess the feasibility of the idea, identify resources, and plan the first steps to move to the next stage. It is often useful to think through the basic elements at this stage business models, which will help to avoid unnecessary costs at the start
💡 Tip: Assess your resources and risks to ensure your idea is sustainable before launching.
2. Infancy
At this stage, maximum involvement of the founder is important, as he is the main driving force of the company. Here the emphasis is on survival and active search for the first clients, and the main task is to minimize expenses and risk. Organizational structure and processes are secondary here, as the focus is on revenue and growth.
Characteristic features: The founder is actively involved in all processes, often replacing the team. Structure and processes are practically absent.
Possible problems: Strong dependence on the founder, chaos, lack of formalization.
Recommendations: Start attracting specialists to the company and transferring tasks to the team.
💡 Tip: Focus on sales and operational sustainability without getting distracted by excessive formalization.
3. Come on, come on
At this stage, the company is actively growing, but the structure often lags behind the dynamics of the business. Here it is important to form a clear business model and consolidate key processes. This is the time of maximum involvement, when it is important not only to increase income, but also to lay the foundation for long-term sustainability.
Characteristic features: The business is growing, the increase in work volumes often outpaces the development of the structure. Increased enthusiasm of the team, but weak control, lack of time for planning.
Possible problems: Employee overload, risk of burnout, resource depletion, chaos in processes, instability due to lack of systematization.
Recommendations: Begin form a stable business model, structure key processes and create rules of interaction within the company.
💡Tip: Develop ground rules and structure to support the company's growth, such as rules for how departments interact.
4. Youth
At the Youth stage, the company faces the need to create a structure and clear business processes. Here, it is important to conduct organizational diagnostics and formalize the strategy. This stage is the period when important decisions must be systematized, which will increase the business's resilience to possible challenges.
Characteristic features: There is a need for a clear structure and management, the company gradually stabilizes. Active implementation of formalization, the beginning of the creation of a company culture, setting tasks and KPIs.
Possible problems: Employee resistance to change, problems with adapting new rules.
Recommendations: Conduct an organizational diagnosisto identify weaknesses and begin to build a corporate culture, develop strategic planning.
💡Advice: Focus on developing and implementing processes that are necessary for stable operation. It is important to implement elements of corporate culture and communication processes.
5. Flourishing
This is the company's "golden age", when it has reached a stable state, a balance of flexibility and structure. At this stage, it is necessary to increase the emphasis on strategic planning to maintain stable growth. The company must have a clear management system and optimally distributed resources. This is the time to actively search for new markets and opportunities.
Characteristic features: Stable growth, high level of productivity, well-established processes, clear goals and strategy, high level of employee motivation.
Possible problems: The risk of losing flexibility and starting to rely on outdated working methods.
Recommendations: Maintain momentum, invest in team development, explore opportunities for diversification and development, continuously improve business processes and strategy.
💡Tip: Invest in innovation and staying competitive by focusing on improving internal efficiency.
6. Stability (Late Bloomer)
This stage occurs when the company maintains its growth, but begins to feel a lack of innovative solutions. The organization maintains stability, but its flexibility gradually decreases. It is important to periodically conduct organizational diagnostics to identify bottlenecks and strengthen the strategic approach. This can prevent stagnation and keep the organization competitive.
Characteristic features: Sustainable development, but a decline in innovative activity, unwillingness to make significant changes. The company is more focused on maintaining the current level than on finding new opportunities.
Possible problems: Risk of stagnation, deterioration of reaction to changes in market conditions.
Recommendations: Conduct regularly organizational diagnostics, strengthen your strategy through innovation and improved customer service.
💡Tip: Develop innovation to keep your company agile and relevant.
7. Aristocracy
At the Aristocracy stage, the organization begins to become more conservative. The emphasis shifts from flexibility to compliance with formal procedures. The main focus is on maintaining the status quo, adhering to traditions. There is a tendency toward excessive formalization of processes, which often suppresses employee initiative.
Characteristic features: The company maintains high standards, but innovation and flexibility are replaced by formal procedures. Emphasis on prestige, possibly excessive attention to the status of the company.
Possible problems: Decrease in growth dynamics, problems with adaptation to new things, risk of loss of competitiveness.
Recommendations: Implement new approaches and motivate employees to find and implement innovative solutions.
💡Advice: Strategy should focus on adaptation and improving operational efficiency while avoiding excessive bureaucracy.
8. Witch Hunt (Early Bureaucracy)
The stage is associated with the recognition of problems that have arisen in the company, but instead of solving them, a search for the guilty begins. Internal conflicts and mistrust make it difficult to make strategic decisions, and the company's productivity falls. Organizational diagnostics is necessary here to identify the sources of problems and determine ways to solve them.
Characteristic features: The company is experiencing growing internal conflicts, mistrust among employees, decreased productivity, and growing discontent.
Possible pproblems: Internal contradictions, demotivation, stagnation.
Recommendations: Conduct a detailed diagnosis to identify problems, review the organizational structure and functions.
💡Tip: It is important to identify the real causes of problems and minimize conflicts before moving forward.
9. Bureaucracy
At the Bureaucracy stage, the company has almost lost its flexibility and innovation. Decisions are made extremely slowly, and the company structure is confused due to a complex hierarchy and many regulations. Innovations and development are practically absent, which leads to a gradual decrease in profitability and cost effectiveness.
Characteristics: Rigid structure that makes adaptation and innovation difficult. Excessive formalization and hierarchy, slow decision-making, high operating costs.
Problems: Low profitability, lack of customer focus, risk of decline.
Recommendations: Review management approaches, minimize redundant processes,
💡Advice: Re-evaluate your company structure and consider making radical changes to eliminate stagnation.
10. Death
The Death Stage symbolizes the complete decline of the company, when it is no longer able to sustain its activities. The business either completely ceases to function, or continues to operate formally, but no longer brings in profit. At this stage, the company is no longer able to adapt to changes, and its existence ends.
Characteristic features: Complete stagnation, loss of relevance in the market, possible cessation of activity. Obsolescence of products and services, loss of target audience, lack of revenue.
Problems: Business failure, resistance to change, inability to adapt.
Recommendations: Either carry out a deep restructuring, or, if recovery is impossible, cease operations.
💡Advice: If an organization has reached this stage, it may be time to look for other opportunities to change direction, launch new projects that can breathe life into the business.
Conclusion
The stages of the organization's life cycle according to the Adizes methodology are a powerful tool for understanding the current stage of a company's development and possible strategies for its further successful functioning.
Knowing these stages helps managers and owners build the right processes, adapt the strategy and effectively manage changes. But determining the stage of development is just the beginning. To successfully pass each stage, it is important not only to understand its features, but also to be able to competently manage a team aimed at the company's growth.
For companies looking to strengthen their management teams and prepare them for the next stage, we offer corporate seminar "Formation and development of management teams"This workshop will help executives and managers understand how to work effectively in a team at each stage of the life cycle and will improve their management competence.
Additionally, to quickly determine the stage of your company's life cycle, you can take our test "Express diagnostics of the life cycle stage according to Adizes"The test results will provide recommendations for the further development of the company and focus on key areas for its sustainable growth.
* Download the test in the "Quick Solutions" section on this page
Prepare for future challenges with professional solutions tailored to your company!